How Community Schools Improve Outcomes
Access the Community Schools section of the Learning Policy Institute website to learn more about the growing body of evidence and momentum for community schools nationwide.
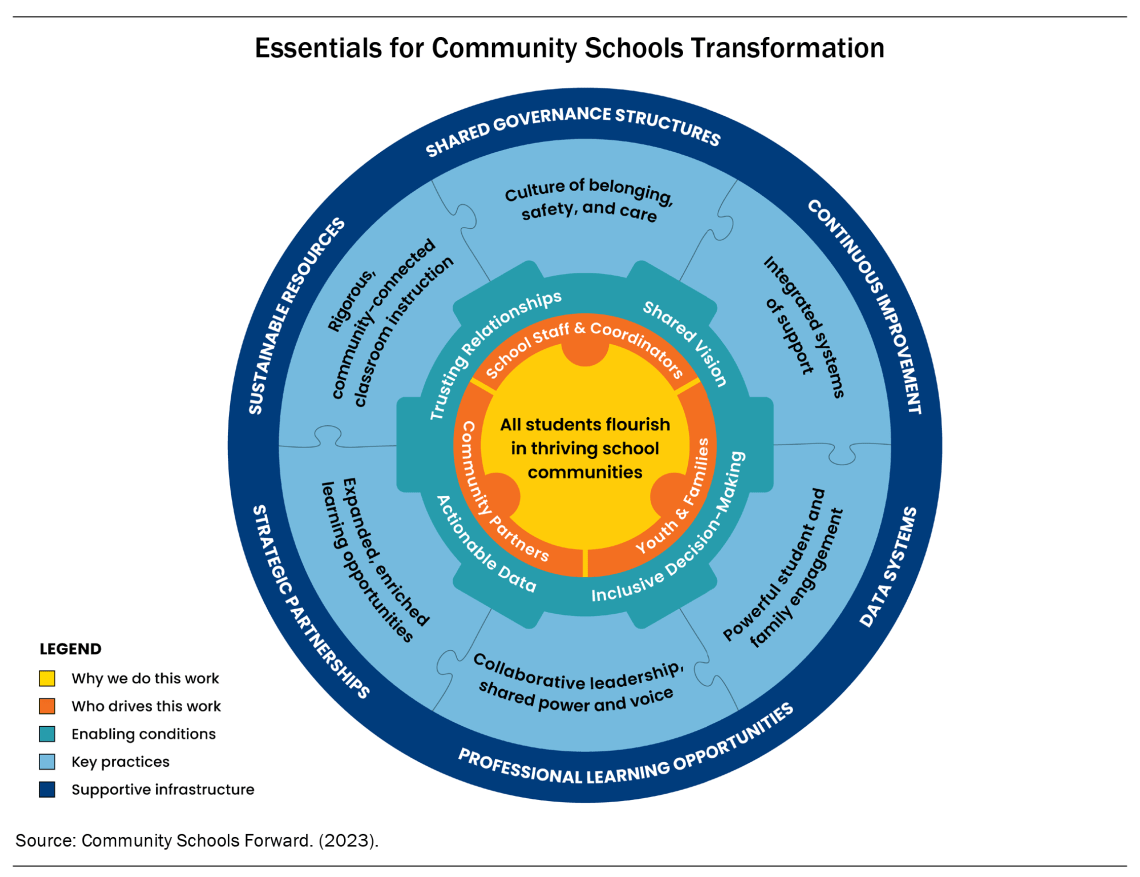
What is a community school?
Using the community schools strategy, public schools partner with families and community organizations to provide well-rounded educational opportunities and in- and out-of-school resources. Through this evidence-based approach, students, families, educators, and community partners come together to support student success. While the specific programs and services (e.g., mental health services, meals, health care) vary according to local context, there are six key practices that form the foundation, or pillars, of community schooling: (1) expanded, enriched learning opportunities; (2) rigorous, community- connected classroom instruction; (3) a culture of belonging, safety, and care; (4) integrated systems of support; (5) powerful student and family engagement; and (6) collaborative leadership and shared power and voice.
In recent years, the federal government and a growing number of states have increased investments in community schools. These include state support through school funding formula allocations, competitive grant programs, and technical assistance resources. In addition, the federal Full-Service Community Schools grant program was increased to $150 million in fiscal year 2025 appropriations. This expanded financial support has been accompanied by a growing evidence base for community schools.
What does research on community schools reveal?
A growing body of research on community schools demonstrates positive outcomes for both students and schools.
Research shows links to improved student attendance, achievement, and school climate.
A 2017 research review examined more than 143 studies, finding that well-implemented community schools led to improvement in student and school outcomes, including:
- Attendance. Improvements in attendance rates and declines in chronic absenteeism are typically among the earliest outcomes of community schools.
- Academic achievement. Decreases in dropout rates and increases in graduation rates often follow, along with improvements in grades and test scores.
- School climate and discipline. An improved school climate is associated with positive relationships, greater school safety, greater engagement with school, and reduced disciplinary incidents and suspension rates.
State investments show similar positive outcomes.
Research on major state and district community school initiatives reinforces the 2017 research review findings and shows how community schools are making a difference for students and families in different locations.
- California. With a historic $4.1 billion investment, California created its Community Schools Partnership Program in 2021. Initial results show that community school sites have effectively reduced their chronic absence rates post-pandemic, and forthcoming research documents improvements in attendance, suspension rates, and achievement for the first grantee cohort.
- Florida. Since 2014, the University of Central Florida has received state funding to administer planning and implementation grants, while supporting grantees through a certification process for its Community Partnership Schools (CPS) model. A study comparing grantee schools in their first year of implementation (2018—19) to similar non-grantee schools found that CPS schools showed improvements in attendance, reductions in disciplinary incidents, and academic improvements for Black students in math and White students in English language arts.
- Maryland. Community schools have been recently included in the school funding formula, which provided $369 million in 2025 for schools with 55% or more students living in poverty to employ community school staff and provide programmatic supports. Recent research shows that community schools have made progress on school climate and attendance outcomes (including reductions in chronic absence rates).
- New Mexico. Since 2019, the state has invested $36.9 million in community schools, including competitive grants and technical assistance. The community schools studied have seen growth in attendance, test scores, graduation rates, student engagement, school climate, health care access, and family engagement.
- New York. Since 2016, community schools have been included in the school funding formula through a set-aside for high-needs districts, along with state-funded technical assistance centers. A RAND study comparing New York City’s 420 community schools to similar non-community schools showed reduced chronic absence and disciplinary rates and improved on-time grade progression and high school graduation. A follow-up study confirmed community schools’ impacts on reducing chronic absence and, after 3 years of implementation, improving math and language arts test scores.
- Ohio. In 2003, Cincinnati residents passed a $480 million bond levy to redesign schools as community hubs. All 65 Cincinnati public schools are now Community Learning Centers. Research and local documentation show districtwide progress from 2006–2015, including a reduction in the achievement gap between Black and White students and substantial increases in 3rd grade reading and high school graduation.
This research was supported by the Ballmer Group.
